Getting Started with Process Hacker
This tutorial will guide you through the basics of using Process Hacker. We'll cover the main interface, navigation, and essential features you need to know to get started.
Step 1: Launch Process Hacker
After installation, launch Process Hacker from the Start menu or by double-clicking ProcessHacker.exe (for portable version). For full functionality, right-click and select "Run as administrator".
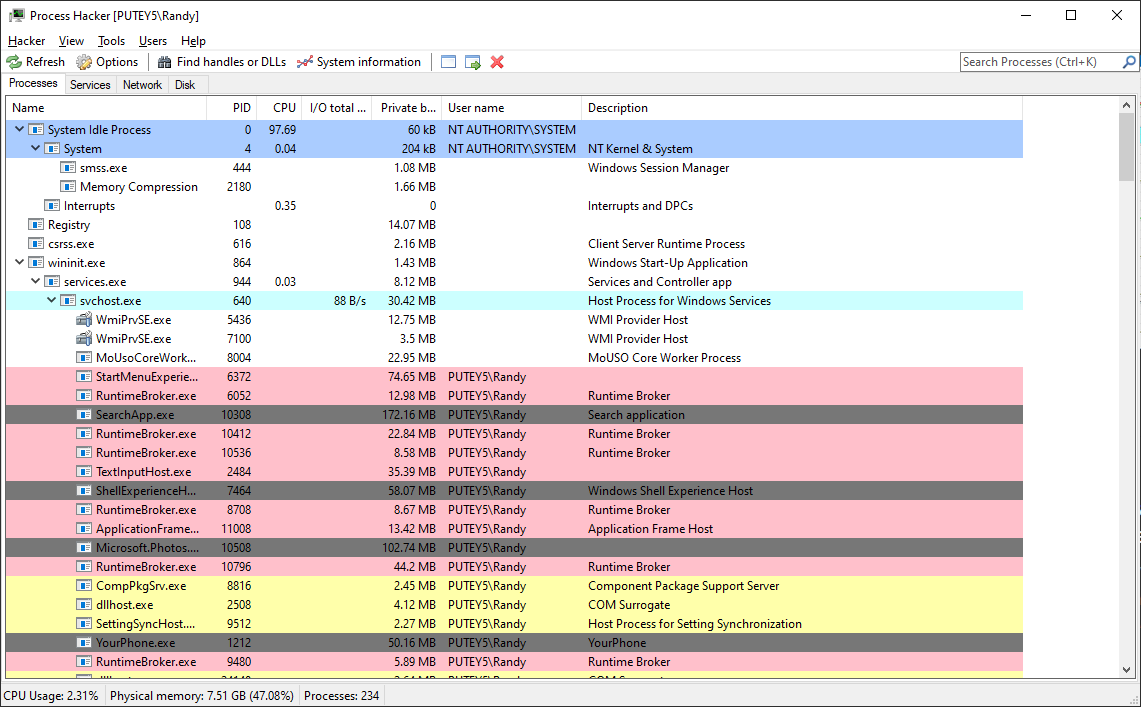
Step 2: Understand the Interface
The main window displays all running processes. Key areas include:
- Process List: Shows all running processes with details like CPU usage, memory, and PID
- System Resource Graphs: Real-time graphs for CPU, RAM, I/O, and Network
- Process Tree: Hierarchical view showing parent-child relationships
- Details Panel: Information about the selected process
Step 3: Navigate and Search
Use the search box to quickly find processes by name. You can filter processes by various criteria using the View menu. Columns can be sorted by clicking on the header.
How to Identify Suspicious Processes
One of Process Hacker's most powerful features is its ability to help identify potentially malicious processes. Here's how to use it for malware detection.
1. Check Process Signatures
Look for processes without valid digital signatures. In Process Hacker, unsigned processes are highlighted. Right-click a process and select "Properties" → "Image" tab to view signature information.
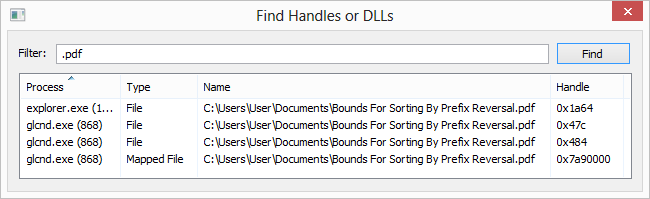
2. Analyze Network Connections
Go to the Network tab to see all network connections. Suspicious processes may have unexpected connections to unknown IP addresses. Check the remote addresses and ports being used.
3. Monitor CPU and Memory Usage
Processes with unusually high CPU or memory usage may indicate malware activity. Use the CPU and Memory columns to sort processes and identify resource-intensive ones.
4. Check Process Location
Malware often runs from suspicious locations like Temp folders or system directories. Right-click a process → Properties → Image to see the full file path. Legitimate processes typically run from Program Files or Windows\System32.
5. Verify Process Details
Use the Properties dialog to check process details. Look for:
- Company name and description fields (often missing in malware)
- Parent process (malware may have unusual parent processes)
- Command line arguments (suspicious parameters)
- Loaded DLLs (unexpected or suspicious DLLs)
How to Terminate Unresponsive Processes
Sometimes processes become unresponsive or need to be terminated. Process Hacker provides several options for ending processes safely.
Method 1: Standard Termination
- Select the process you want to terminate
- Right-click and select "Terminate" or press Delete
- Confirm the termination in the dialog box
Note: This sends a termination signal. If the process doesn't respond, use "Kill" instead.
Method 2: Force Kill
- Select the unresponsive process
- Right-click and select "Kill" (or press Shift+Delete)
- This immediately terminates the process without allowing it to clean up
Warning: Force killing may cause data loss. Use only when necessary.
Method 3: Suspend Process
For troubleshooting, you can suspend a process temporarily. Right-click → "Suspend" pauses the process. Right-click → "Resume" to continue it. This is useful for isolating problematic processes.
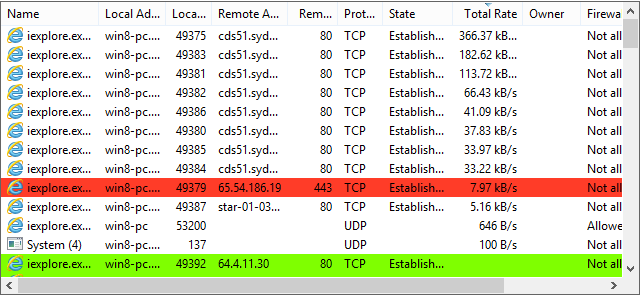
How to Monitor Network Connections
Process Hacker's network monitoring feature helps you track all network activity on your system, identify which processes are using the network, and detect unauthorized connections.
Accessing Network Information
- Click on the "Network" tab in the main window
- View all active network connections, both TCP and UDP
- Each connection shows the process, local address, remote address, state, and protocol

Understanding Connection Details
- Local Address: Your computer's IP and port
- Remote Address: The external IP and port being connected to
- State: Connection state (LISTENING, ESTABLISHED, TIME_WAIT, etc.)
- Protocol: TCP or UDP
- Process: The process using this connection
Identifying Suspicious Connections
Look for:
- Connections to unknown or suspicious IP addresses
- Processes with unexpected network activity
- High number of connections from a single process
- Connections on unusual ports
How to Analyze System Performance
Use Process Hacker to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize your system. The resource monitoring features provide detailed insights into system resource usage.
CPU Usage Analysis
- Sort processes by CPU usage to find resource-intensive processes
- View the CPU graph for overall system CPU usage
- Check per-core CPU usage in the graph view
- Identify processes with sustained high CPU usage
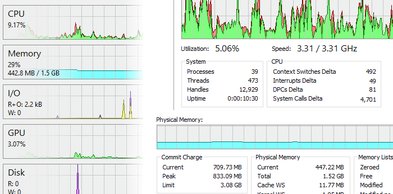
Memory Analysis
- Monitor physical memory usage and commit charge
- Sort by memory usage to find memory-hungry processes
- Check working set, private bytes, and virtual memory
- Identify memory leaks by monitoring growing memory usage
Disk I/O Monitoring
- View disk read/write operations per process
- Monitor disk throughput and I/O rates
- Identify processes causing excessive disk activity
- Use I/O statistics to optimize disk performance
Performance Optimization Tips
- Close unnecessary processes to free resources
- Adjust process priorities if needed (use with caution)
- Identify and remove resource-intensive background services
- Monitor resource usage over time to identify patterns
Advanced Usage Tips
Service Management
Use the Services tab to manage Windows services. Start, stop, pause services, and modify startup types. View service dependencies and properties.
Process Properties
Double-click any process to view detailed properties including threads, handles, memory regions, loaded modules, and environment variables.
Filtering and Searching
Use the search box and filters to quickly find processes. Filter by name, CPU usage, memory usage, or other criteria. Save filter presets for common searches.
Keyboard Shortcuts
- Delete: Terminate selected process
- Shift+Delete: Kill selected process
- F5: Refresh process list
- Ctrl+F: Search for process
- F2: Rename process (if applicable)