Published: January 15, 2024 | Category: Security
How to Detect Malware Using Process Hacker
Process Hacker is an invaluable tool for detecting malware and suspicious processes on your Windows system. This comprehensive guide will teach you the techniques and strategies used by security professionals to identify and eliminate threats.
Traditional antivirus software relies on signature-based detection, which can miss new or sophisticated malware. Process Hacker provides real-time monitoring and detailed analysis capabilities that allow you to identify suspicious behavior patterns that antivirus might miss.
Key Indicators of Malware
- Processes running from temporary folders or suspicious locations
- Unsigned processes (missing digital signatures)
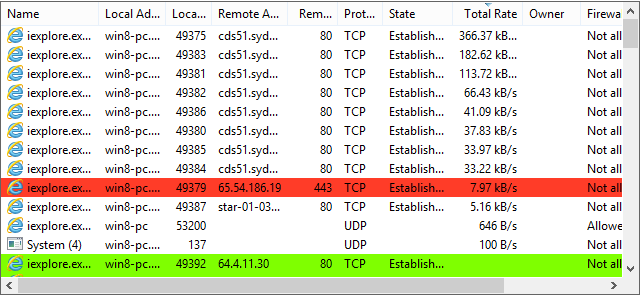
- Unusual network connections to unknown IP addresses
- High CPU or memory usage from unknown processes
- Processes with suspicious command-line arguments
- Processes hiding themselves or using rootkit techniques
Step-by-Step Detection Process
Start by examining processes for digital signatures. Legitimate software is typically signed, while malware often lacks proper signatures. Use Process Hacker's Properties dialog to check signature information. Next, monitor network connections to identify unauthorized communication. Malware frequently communicates with command-and-control servers or exfiltrates data.
Analyze process memory usage and behavior patterns. Malware often consumes resources inefficiently or shows unusual patterns. Use Process Hacker's detailed memory view to examine process memory regions and identify suspicious activity.
Read the full tutorial →
Published: January 10, 2024 | Category: Comparison
Process Hacker vs Task Manager: Complete Comparison
While Windows Task Manager is useful for basic process management, Process Hacker offers advanced capabilities that make it the superior choice for power users, system administrators, and security professionals.
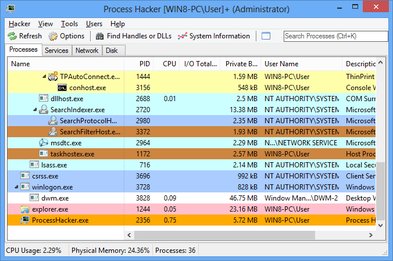
Task Manager provides basic process information and termination capabilities, but Process Hacker goes far beyond with detailed process properties, network monitoring, service management, memory analysis, and debugging capabilities. This comprehensive comparison highlights the key differences and explains when Process Hacker is the better choice.
Feature Comparison
Process Hacker excels in network monitoring, providing detailed TCP/UDP connection information that Task Manager completely lacks. For system administrators managing services, Process Hacker's integrated service management is far more comprehensive than Windows Services Manager. Memory analysis capabilities in Process Hacker allow deep inspection of process memory, while Task Manager only shows basic memory statistics.
When it comes to process termination, Process Hacker offers multiple options including suspend, resume, and force kill capabilities that aren't available in Task Manager. The ability to view process trees, thread information, and handle details makes Process Hacker essential for debugging and system analysis.
View all features →
Published: January 5, 2024 | Category: Performance
System Performance Monitoring Best Practices
Effective system performance monitoring requires the right tools and techniques. Process Hacker provides comprehensive resource monitoring that helps identify bottlenecks and optimize system performance.
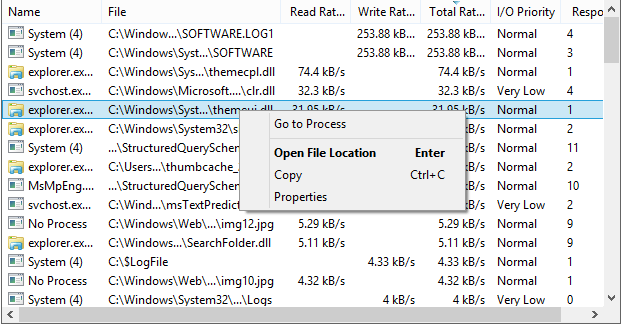
Understanding how to interpret Process Hacker's resource graphs and statistics is crucial for effective performance monitoring. This guide covers best practices for monitoring CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network activity to maintain optimal system performance.
Monitoring Strategies
Establish baseline performance metrics during normal operation. Use Process Hacker's historical graphs to identify trends and patterns. Monitor resource usage during peak times to identify capacity limits. Set up alerts for critical thresholds to catch performance issues early.
Regular monitoring helps identify memory leaks, CPU hogs, and inefficient processes. Process Hacker's detailed per-process statistics make it easy to pinpoint the exact source of performance problems and take corrective action.
Learn more about performance monitoring →


